Hi! This is Jane, founder of Discover with Jane marketing agency. This is my weekly newsletter about marketing hacks, trends, and startup growth.
If you prefer watching, here is the link to video version of this newsletter.
Today we’re talking about SEO.
SEO might seem intimidating. Domain rating, domain authority, keyword density, backlinks, SERP, and many other scary words. And where should you get those backlinks and metrics from?
In this newsletter I'm explaining:
process of search engine optimization start to finish
how SEO in 2024 differs from 2008, and what key parts there are
how SEO helps understand your customer's intentions
types of search results, and what AI got to do with it
tools for SEO keyword research
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of getting your website to the top of search results on Google, or other engine (think YouTube as #2 search engine).
You start your business newsletter, website or blog. By the way, companies with blogs get 67% more leads. But how do you make your blog visible to people?
How the SEO process evolved
First thing to understand, is that SEO process is changing. Right now I'm re-learning SEO, and taking you on this journey with me!
One of my first jobs was a SEO-copywriter. Back in 2008 is was in college. After classes, I started preparing SEO texts for different websites. And back then, the process looked like this:
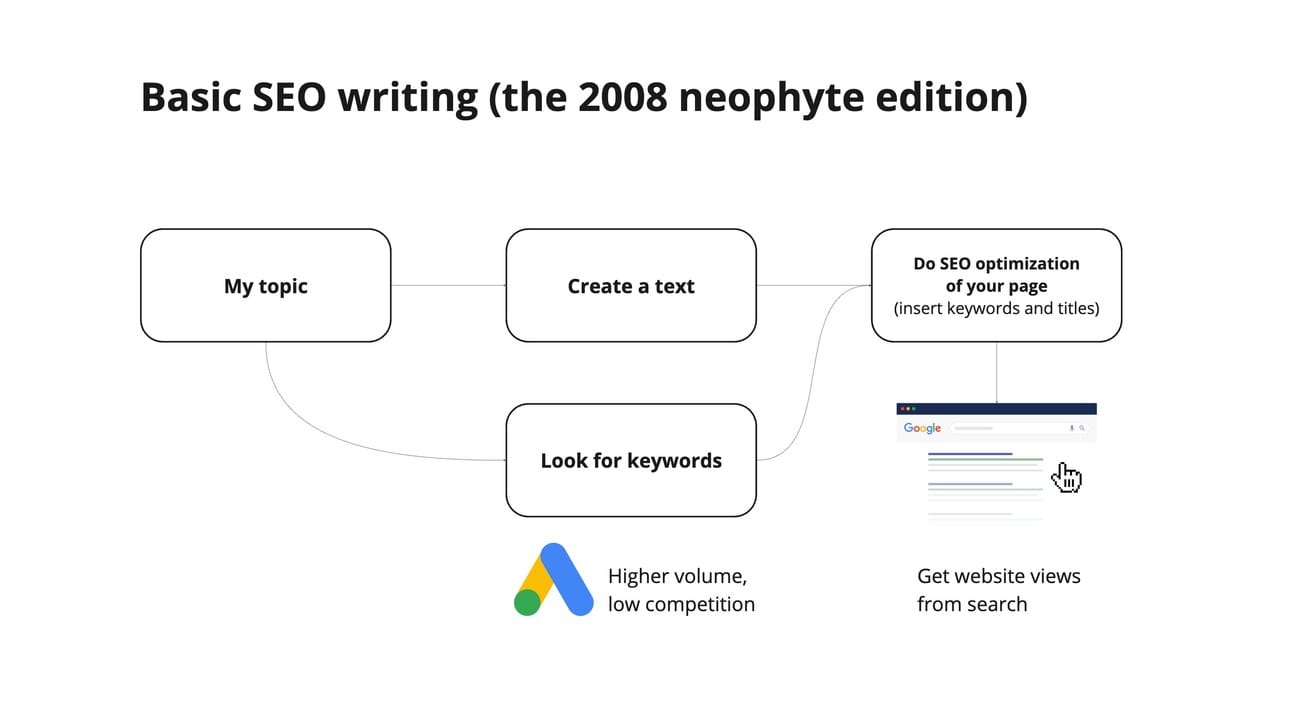
First, you used to receive the topic, the keywords that they wanna use (optionally) or just the different subtopics.
Second, you would research the topic and write the text — optimizing it with inserting the keywords.
And this was really how SEO optimization looked like.
Today this process still exists, so it's still valid. It's called on-page SEO, but SEO in 2024 is much more complicated. Like this:
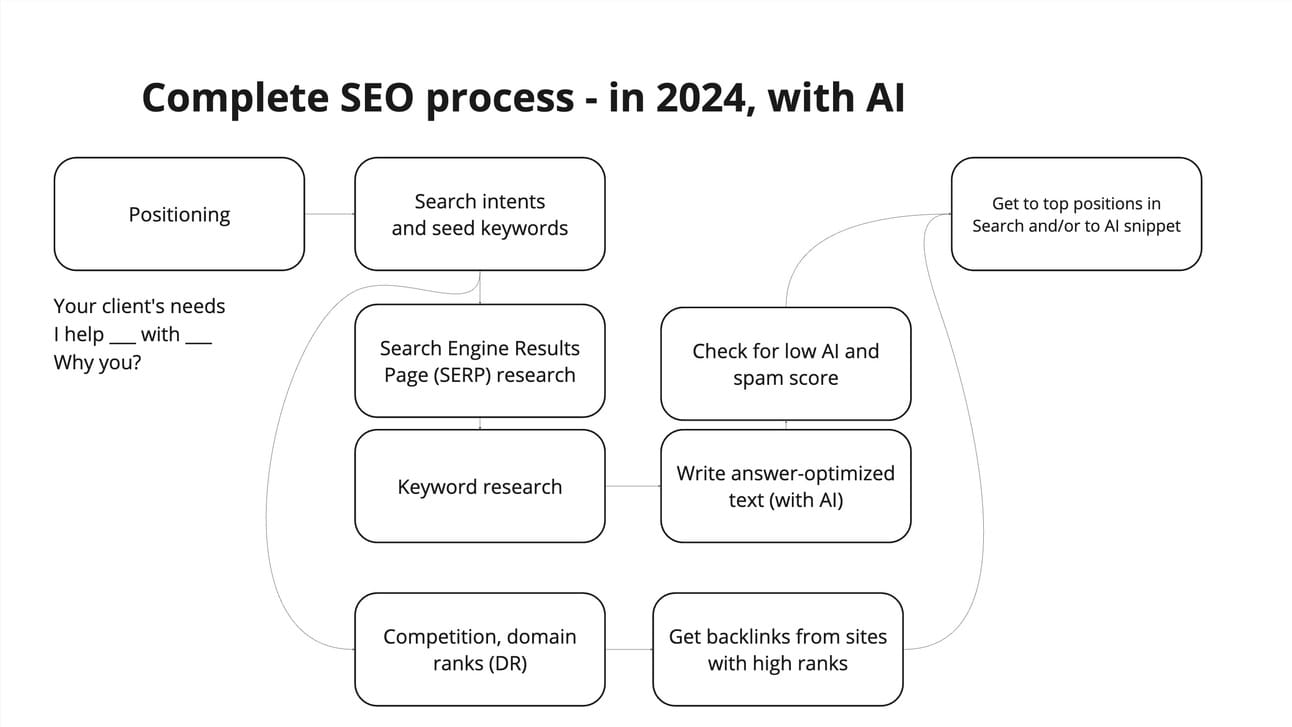
We see that technologies, namely AI, and constant evolution of algorithms broght tremendous changes to the SEO process. And it’s not only about AI generating your content. It’s also AI making the search results.
7 main pillars of SEO in 2024
#1 Positioning. It all starts with positioning. The topic of positioning is like the big WHY of marketing and search. Why are users looking for what they’re looking for in the first place? You need to understand your client's needs and what kind of service you offer.
#2 Search intent. Search intent is the user’s intention, the task they are completing. Simply put, search intent is the way people talk to Google, what they type in when they are looking for your type of product. And this is what is meant by seed keywords.
Knowing the search intent, you can ask AI tools to generate your keywords. Alternatively, you can see versions of the question in the "People also ask for” section.
#3 SERP. Once you understand what your seed keywords are, you look at the results pages, which is SERP. Search Engine Results Page or SERP is what the user sees, when they input their search into Google. And this is also your competitive field where you’re trying to do better than your competitors.
Right now there are like 15 different kinds of SERP:
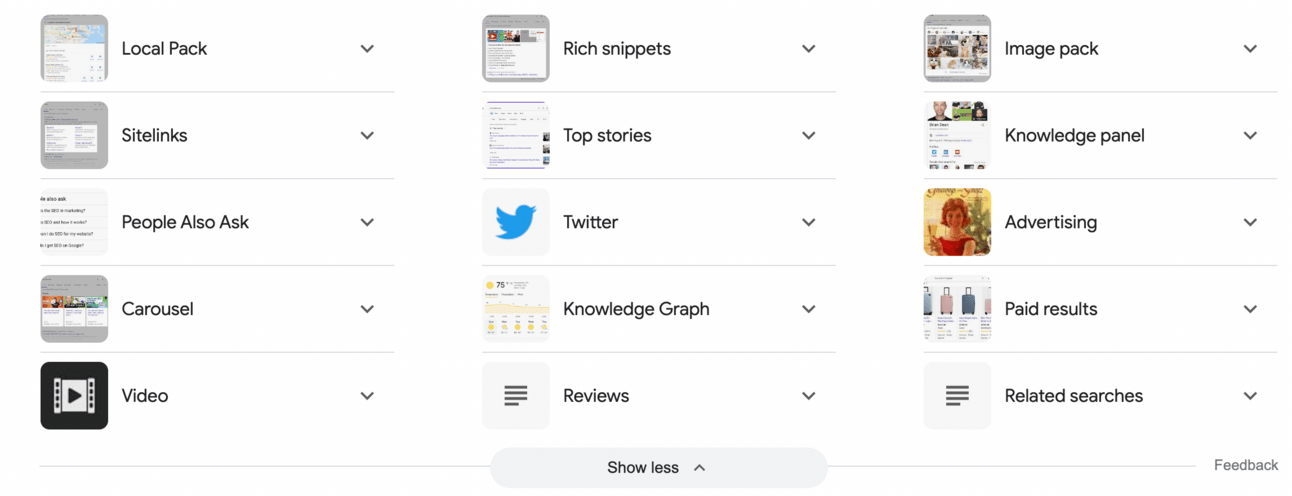
Source: Google Search
#4 Keywords. Then you do keyword research. You compare different keywords (easier to tackle where there is lower competition). You might also want to look for competing websites. There are metrics like domain ranks — you are going to compare those rankings to yours and see if you have a chance to rank on certain keywords.
#5 Anwer-optimised text. Here you are writing the answer optimized text — the answer optimization is a huge part of search engine optimization in 2024.
#6 Backlinks. When you have finished working on your page, you need to get as many links from other websites to your website as possible. In this way Google understands that they trust you more. And this is how your page ranks higher.
#7 Metrics. When you are done with writing and checking, you should monitor the metrics. You should be looking at increasbing the number of backlinks and your positions in search results.
Below we will consider the main points in detail.
Search intent in SEO 2024
The search intent is what people are looking for. What's is important is to match your search intent with the keywords you are using.
Satisfying the search intent is a primary goal for search engine optimizers. When the user search for some term, it's important for Google to give them a type of results which they're going click on. So it should match what the user is looking for.
Example: If you were a person looking for hotels, you probably wouldn't type the word “accommodation” or something like that. You will just type “book a hotel.”
4 types of search intents
There are 4 major types of search intents. Let's look at each of them:
Informational
Not all search intents are targeted at buying something. There are informational types of search intents, when you are looking for an answer of how old George Clooney is, or what the population of New York is. When you're looking for what SEO is, or how to get on top of Google — this is also an informational intent.

Preferential/Commercial Investigation
This is the type of intent where people are comparing one option versus the other one. For example, which hotel is better, or which website offers better hosting service.
Transactional
It might look like “buy this kind of bag” or “purchase SEO analytics tool”. Words buy or purchase are not necessary.
Many brands prefer to compete for these type of keywords. And this is what they usually buy for promotional keywords in Google Ads. But this is usually not the best place to start because if people don't know your brand, they are not going to click this.
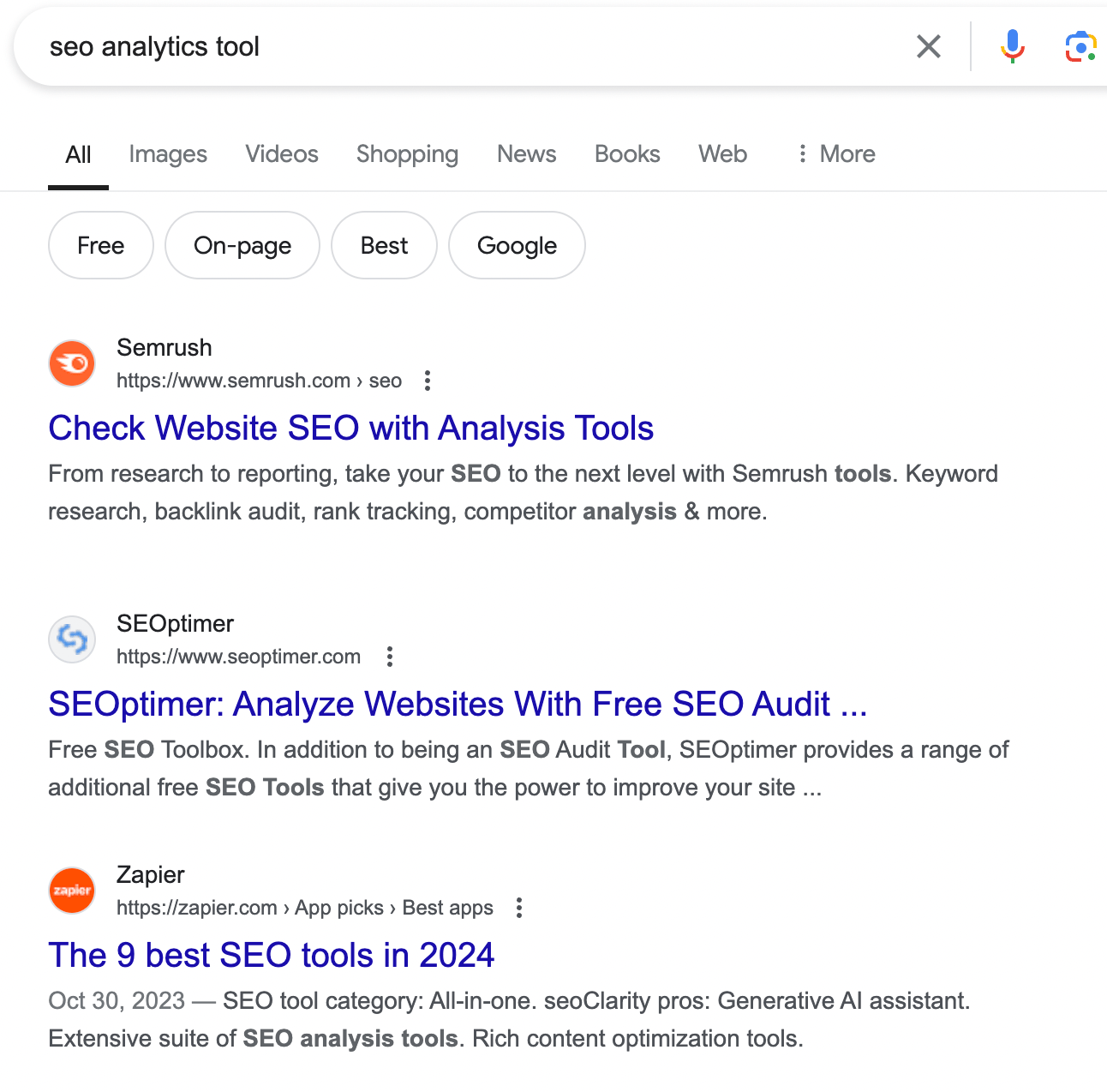
Navigational
Do you remember the time where you wanted to get to a certain website and instead of just following a link or typing the link into the browser, you type it in Google. For example, “Booking login”. So you want to go to booking.com. You can go to a direct link, but instead, you would type it in Google
When you understand your search intent, the type of it — for example, you have an informational serach intent, you are looking for info on how to choose a marketing agency — you literally input that into Google and you see how it looks like:
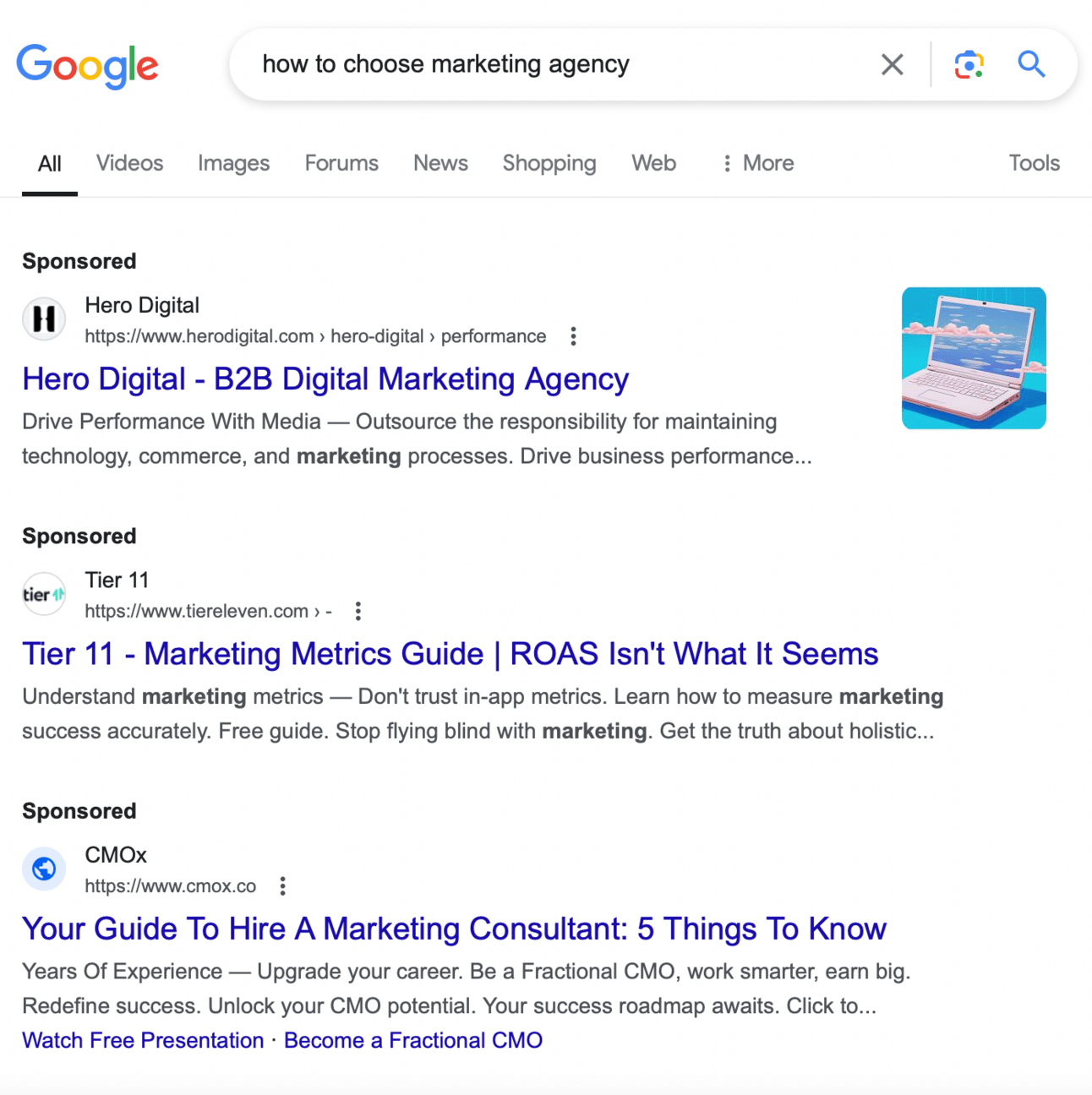
Source: Google Search
You see 4 sponsored results. People are paying to be on top of minds of the people who are choosing a marketing agency. You might visit their page and if the article is good, you might read it, but you're not shopping yet.
The 2nd result, looking like a valuable guide, is better for this kind of search. THe intent is informational. Most people won’t buy your service after they go to your page from here. But if you give value - they might choose you later.
The shopping page for the same agency would look like “Hero Digital marketing agency”, when people already know about this agency.
Types of SERPs
When you understand your keywords, or rather different types of keywords, you can go to Google search pages and see what the results page looks like for each of them.
To give you an explanation why it's important, we need to go back to the early days of the internet. In the old days, all search results looked the same. The blue lines of links with descriptions. And this was the search as a librarian: “here is what we’ve found about your topic." But the person had to make the decision, which link answers the question better, and is therefore more relevant.
Our modern user equipped with ChatGPT doesn’t simply want the blue links. They want answers to their questions! And this is exactly what LLM do for her — choosing and sorting out.
Google is evolving as well. It is trying to be helpful. The goal is to make a person click on the website. That's why they are introducing more and more different types of SERP:
Source: Google Search
Local pack, which is location specific.

The “people also ask” section, which is a collection of questions related to yours.

Related searches — similar to “people also ask”.
Different types of collections: site links, carousels, the top stories. Something like you would get when searching for best books on a topic.

The knowledge graph — something that you might see when you Google for weather, for example.
Knowledge panels — usually pop out when you Google a person or an event.

Image packs or videos when you're looking for visuals.
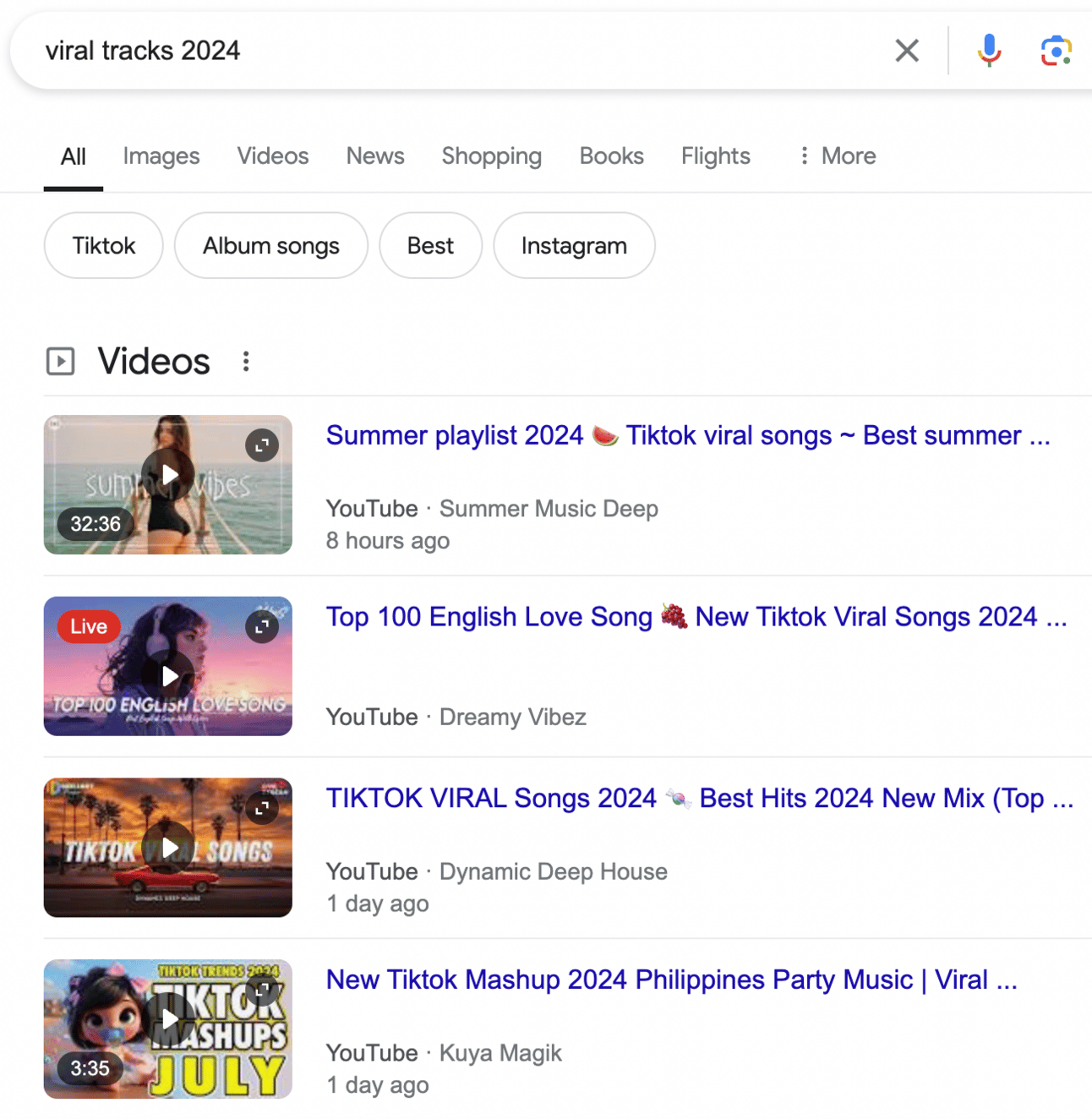
Paid results in advertising — those are important for us, we understand that those advertising or sponsored types of content are preferred because people paid for it.
A rich snippet — an important type of SERP, which interests us with the rise of AI.
The answer snippet is AI-driven type of search. What Google does here is they provide not the collection of links so that the person can choose their preferred answer. Instead, they generate the answer for the user. It looks like a short summary called “featured snippets” and you see under search results. These snippets give you a quick idea of a webpage, so you can decide if you want to visit it.
Competing with Chat GPT and other AI tools, Google went further and introduced short AI summaries (or “AI overviews”) that appear at the top of search results to answer your question quickly and tailored to your request. They come from websites that Google thinks are relevant. You can see an example of this in the image below.

Why is it important for us? It gives a chance to people or websites who answered the question in the best possible way to be on top of Google. So when you look at the SERP, you need to see if there is an AI snippet:
If there is one, you need to target your page towards answering that question for which there is a snippet. And you need to answer the question precisely and concisely, in the most useful way & in 300 words approximately.
If there are sponsored results, this means that there is a lot of competition for this topic and with your organic text not being sponsored, you're not going to be seen.

Keywords research
After we've looked at the SERP, we understand which search results & keywords are better than the others.
What else you can do is you can use certain services for comparing one keyword to another one. For this, you can use Google Keyword Planner.
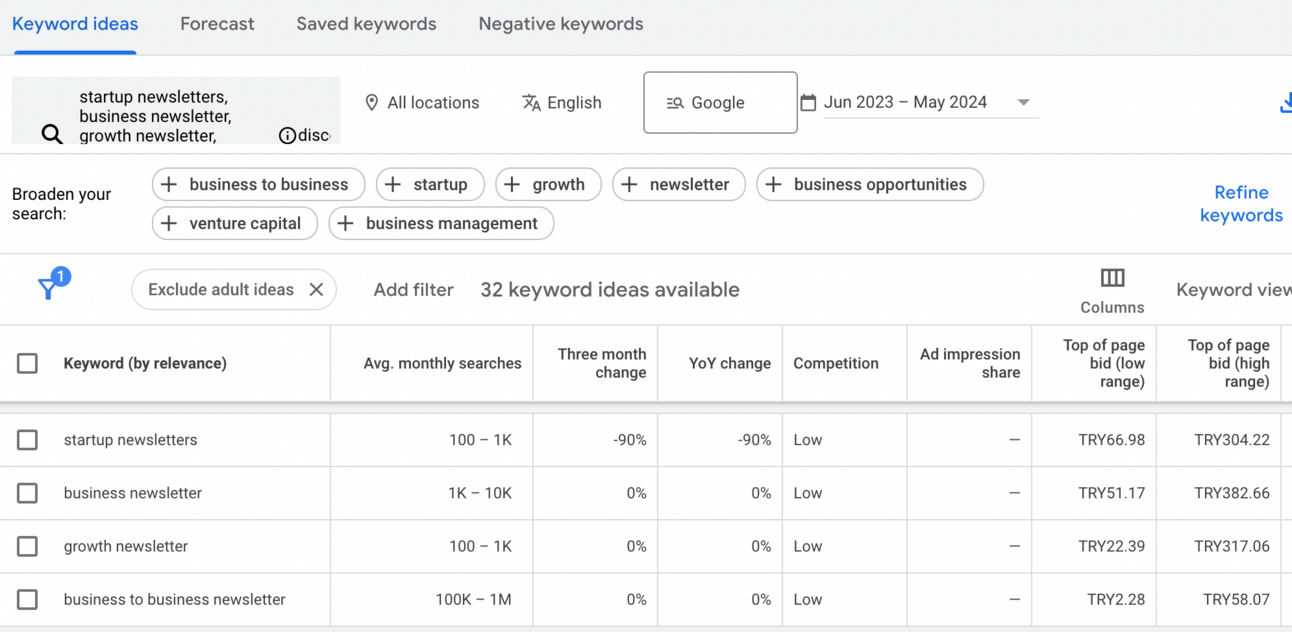
This is how it looks like. You can see average monthly searches for the term you have chosen. You can compare them between one another. The levels of competition can be low, medium or high. You can also see an approximate cost if you choose paid promo.
Similar tools — Mangools:
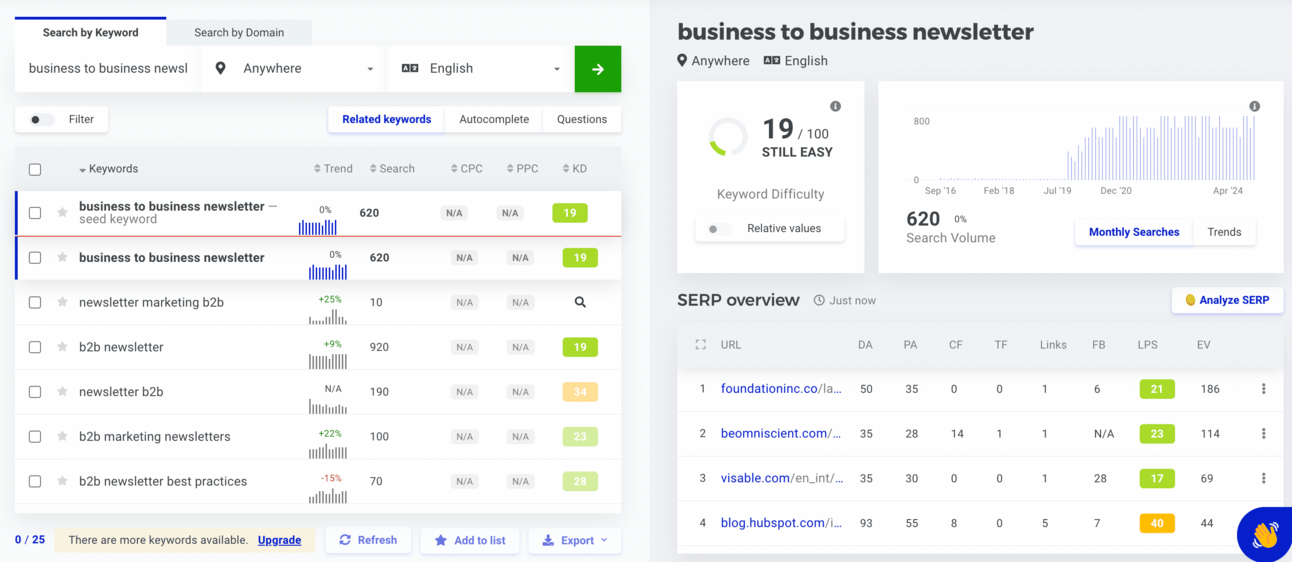
What is more important in SEO ranking is that they provide you with the domain rating of your competitors. And by comparing your rating with the competition, you see if you possibly could be competing in the niche of this keyword.
It's useful to make a table out of those instruments because sometimes you can see that two keywords have the same number of searches, but one of them is much less competitive than the other. Then because they sound similar, you should try to compete where the competition is lower. Or they could have the same competition, but one of the words has far more search results. Of course, get the one with more search results.
For one page you need around 10 keywords on a similar topic because you cannot fit a lot of words.

I’ve decided to split the SEO topic into 2 parts, so that you do not get overwhelmed with this topic.
In the next newsletter on the SEO topic, I'll tell you more about domain ratings. How websites compete against each other, which tools there are to measure domain rating, and what backlinks got to do with it!
Thank you for reading this newsletter. Subscribe to my YouTube Channel not to miss the new episodes.
Next week’s topic is going to be fun: the Olympic Games are coming, and the olympic marketing trends!
See you next week,
Jane

